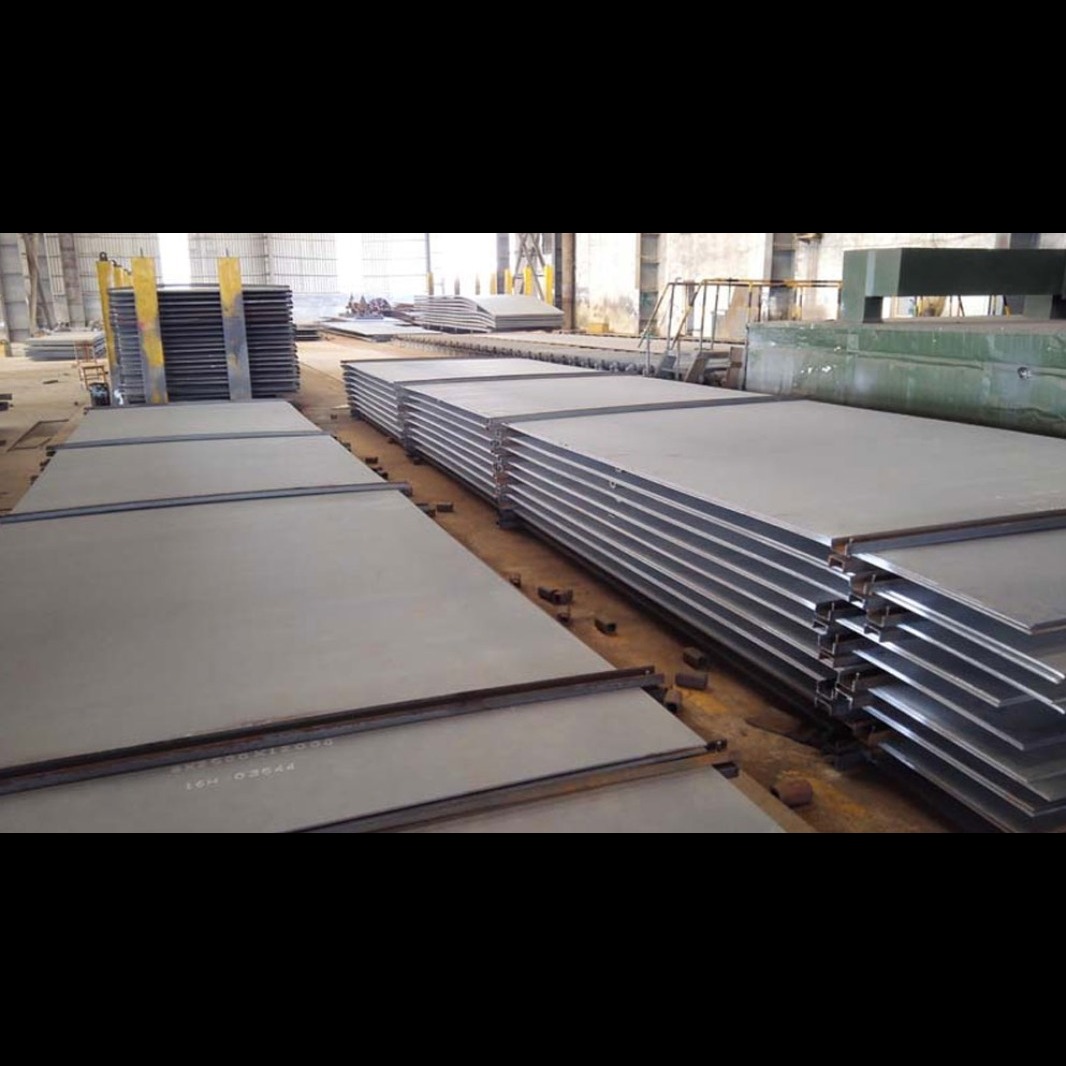
Alloy Steel – Engineered Strength for High-Stress Applications Alloy Steel is a specialized category of steel enhanced with elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, and manganese, giving it superior strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and wear. These steels are carefully formulated to perform under extreme conditions where standard carbon steel would fall short. From high-temperature boilers to heavy-duty shafts and gears, alloy steels are known for their reliability, toughness, and adaptability, making them essential in power generation, oil and gas, heavy engineering, and aerospace sectors. Benefits of Alloy Steel: High mechanical strength and durability under pressure Excellent performance in elevated temperatures and corrosive environments Greater resistance to fatigue, wear, and impact Can be tailored to meet specific mechanical or metallurgical requirements Supports heat treatment for enhanced performance Types of Alloy Steel: Low Alloy Steel: Contains lower alloying element content (usually <5%) High Alloy Steel: Contains higher proportions of elements for niche or extreme applications Key Alloying Elements & Effects: Element Enhances Chromium Corrosion resistance, strength, hardness Nickel Ductility, impact strength, corrosion resistance Molybdenum High-temperature strength, creep resistance Vanadium Toughness, shock resistance, wear resistance Manganese Hardenability, strength, deoxidation Boron Improves hardenability with small additions Typical Mechanical Properties: Property Range (Approx.) Tensile Strength 400 – 1300+ MPa Yield Strength 250 – 1000+ MPa Elongation 10% – 25% Hardness Up to 60 HRC (depending on treatment) Fatigue Resistance High Popular Alloy Steel Grades: SA 387 Gr. 5, 9, 11, 22, 91 – for high-pressure, high-temperature service EN 19 / EN 24 / EN 31 – for shafts, tools, automotive parts AISI 4130 / 4140 / 4340 – for aerospace, forgings, drilling rigs P11 / P22 / T91 / 16Mo3 – for boilers, power plant tubes Industries Served: Power and thermal plants – for pressure-bearing components Oil & gas – pipelines, heat exchangers, processing units Heavy machinery – shafts, gears, pins, tooling Automotive and railways – axles, suspensions, crankshafts Aerospace & defence – high-stress precision components Conclusion: Alloy Steel is the go-to choice for critical applications that demand high performance under stress. Whether exposed to high heat, corrosive media, or mechanical load, alloy steel delivers strength, reliability, and extended life, making it an irreplaceable material in modern engineering.
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
https://www.alloysteelsplate.com/latest-update/alloy-steel-engineered-strength-for-high-stress/115
Alloy Steel – Engineered Strength for High-Stress ...

2025-06-20T05:02:32
Alloy Steel – Engineered Strength for High-Stress Applications Alloy Steel is a specialized category of steel enhanced with elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, vanadium, and manganese, giving it superior strength, hardness, and resistance to heat and wear. These steels are carefully formulated to perform under extreme conditions where standard carbon steel would fall short. From high-temperature boilers to heavy-duty shafts and gears, alloy steels are known for their reliability, toughness, and adaptability, making them essential in power generation, oil and gas, heavy engineering, and aerospace sectors. Benefits of Alloy Steel: High mechanical strength and durability under pressure Excellent performance in elevated temperatures and corrosive environments Greater resistance to fatigue, wear, and impact Can be tailored to meet specific mechanical or metallurgical requirements Supports heat treatment for enhanced performance Types of Alloy Steel: Low Alloy Steel: Contains lower alloying element content (usually <5%) High Alloy Steel: Contains higher proportions of elements for niche or extreme applications Key Alloying Elements & Effects: Element Enhances Chromium Corrosion resistance, strength, hardness Nickel Ductility, impact strength, corrosion resistance Molybdenum High-temperature strength, creep resistance Vanadium Toughness, shock resistance, wear resistance Manganese Hardenability, strength, deoxidation Boron Improves hardenability with small additions Typical Mechanical Properties: Property Range (Approx.) Tensile Strength 400 – 1300+ MPa Yield Strength 250 – 1000+ MPa Elongation 10% – 25% Hardness Up to 60 HRC (depending on treatment) Fatigue Resistance High Popular Alloy Steel Grades: SA 387 Gr. 5, 9, 11, 22, 91 – for high-pressure, high-temperature service EN 19 / EN 24 / EN 31 – for shafts, tools, automotive parts AISI 4130 / 4140 / 4340 – for aerospace, forgings, drilling rigs P11 / P22 / T91 / 16Mo3 – for boilers, power plant tubes Industries Served: Power and thermal plants – for pressure-bearing components Oil & gas – pipelines, heat exchangers, processing units Heavy machinery – shafts, gears, pins, tooling Automotive and railways – axles, suspensions, crankshafts Aerospace & defence – high-stress precision components Conclusion: Alloy Steel is the go-to choice for critical applications that demand high performance under stress. Whether exposed to high heat, corrosive media, or mechanical load, alloy steel delivers strength, reliability, and extended life, making it an irreplaceable material in modern engineering.
2025-06-20T05:02:32
Keywords
- fatigue wear
- irreplaceable material
- critical applications
- goto choice
- thermal plants
- 60 hrc depending
- higher proportions
- elevated temperatures
- reliability toughness
- heavyduty shafts
- hightemperature boilers
- fall short
- extreme conditions
- carefully formulated
- manganese giving
- specialized category
- modern engineering
- adaptability making
- steel enhanced
- gears alloy steels
- extended life making
- enhanced performance types
- gas heavy engineering
- standard carbon steel
- demand high performance
- meet specific mechanical
- pressure excellent performance
- aerospace sectors benefits
- power generation oil
- superior strength hardness

Submit Your Enquiry